Webb mirrors collect light from the sky and direct you to scientific tools. Tools that filter light, or scatter it spectroscopically, before finally focusing on the finders. Each tool has its own icons. Finders are where photons were absorbed and eventually converted to electrical energy we measure.
James Webb Telescope needs more sensitive detectors to record dim light from distant galaxies, stars, and planets. It requires large space cameras to successfully scan the sky.
Webb expanded – the state of the art infrared detectors – by producing the same components with lower noise, larger format, and longer lasting than their predecessors.
Webb’s Unique Infrared Detectors
Webb uses two different types of detectors: Near-infrared Detectors and Mid-Infrared Detectors, mercury-cadmium-telluride (abbreviated HgCdTe) “H2RG” 0.6-5 μm “near-infrared” and arsenic mixed silicon (abbreviated in Si: As)) of 5-28 μm “medium infrared”.
Near-infrared detectors were made by Teledyne Imaging Sensors in California. “H2RG” is the product name of the brand Teledyne. Mid-infrared detectors were manufactured by Raytheon Vision Systems, also located in California. Each Webb H2RG detector contains about 4 million pixels. Central infrared detectors contain approximately one million pixels each.
With a better view of the first universe, NASA said in a separate release last year about Webb’s infrared capabilities, astronomers hope to gain more insight into how galaxies formed and evolved.
Read: NASA Hides James Webb’s First Target. Why, Let’s Find Out
How Will Infrared Light Help Webb To Look Into Deep Space?
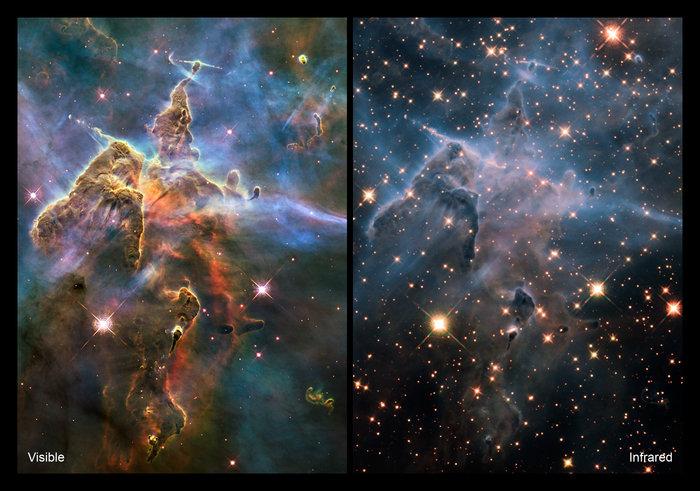

Since infrared light is less likely to be disturbed by dust, Webb will also enable astronomers to observe what is happening inside dust clouds in the vicinity. “We can enter into the dust and see the processes that lead to the formation of stars and planets,” the ESA statement said.
This means that, for example, Hubble’s 2020 vision of the Eagle Nebula “Creative Pillars” in infrared may look different from Webb’s infrared view. Pillars is a popular star-studded site, where Webb can offer more insights.
“The formation of stars throughout the universe takes place amid dense, dusty clouds, hidden from our view by ordinary visible waves,” ESA said in a statement.
Using infrared light, the Webb telescope will be able to look back in time more than the front telescopes, and it will allow scientists to look at the dust to see which stars are building inside.
Also read: Do Aliens Exist: How JWST Will Solve Its Major Launch Objective?
Why Is James Webb Space Telescope Focused Only On Infrared?

Paul Geithner provides insight into why the Webb telescope is focused on infrared.
Infrared light has electromagnetic radiation with longer wavelengths than visible light but shorter than radio waves.
Hubble, for example, can see 13.3 billion years ago, shortly after the creation of the universe. Webb, on the other hand, will be able to look even farther, absorbing six times the amount of light and allowing 100 times more magnification. Webb also has 15 times the viewing field on its camera than Hubble.
Read more about JWST
