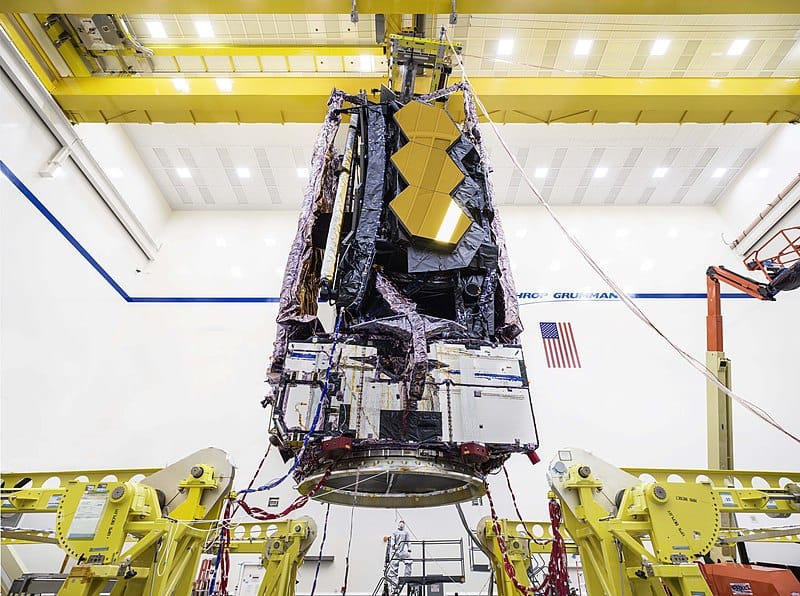
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is set up for launch on 22 December. Is preparing to launch its most ambitious space telescope or mission ever later this month. Engineers working on the launch of the James Webb Orbit Telescope have finished the complex procedure to load the fuel it will require to propel itself while in space, according to NASA.
The engineers are now ready to deploy the folded equipment into the top of a rocket, which is scheduled to launch later this month to place the telescope in orbit.
NASA and the European Space Agency collaborated on the Webb telescope project. Its purpose is to reveal the evolution of the cosmos from its beginnings to the current period.
It will study the cosmos exhaustively at infrared wavelengths and will become the principal workhorse, replacing the aging Webb Space Telescope, which has done this work for the past 30 years.
The countdown to the launch on 22 December has begun again
NOVEMBER 24, 2021 UPDATE NASA said today that engineering teams performed further testing to determine that the James Webb Space Telescope is ready for flight. As a result, launch preparations have resumed. Webb’s official launch date has been set for December 22 at 7:20 a.m. NASA issued the following statement:
Following an occurrence in which the loosening of a clamp band caused a vibration across the observatory, more testing was performed this week to ensure the observatory’s health.
On Wednesday, November 24, design engineers completed these tests, and a NASA-led anomaly assessment board confirmed that no observatory components were affected in the event.
There was an agreement to do a fuel evaluation. And NASA gave the go-ahead to start fuelling the observatory. Fueling activities will begin on Thursday, November 25, and will last around ten days.
The launch date had been set for December 18, 2021. NASA has said that the launch will now take place no sooner than December 22. The whole statement is as follows:
Related: Why is the James Webb telescope better than Hubble?
Launch somewhere near the Planet’s surface
NASA said in the summer of 2021 that the telescope will ship to the launch site in August “with little to no scheduling margin.” With such a short timeline, the telescope would not be ready for launch until October 31. In September, a new launch date of December 18, 2021, was revealed.
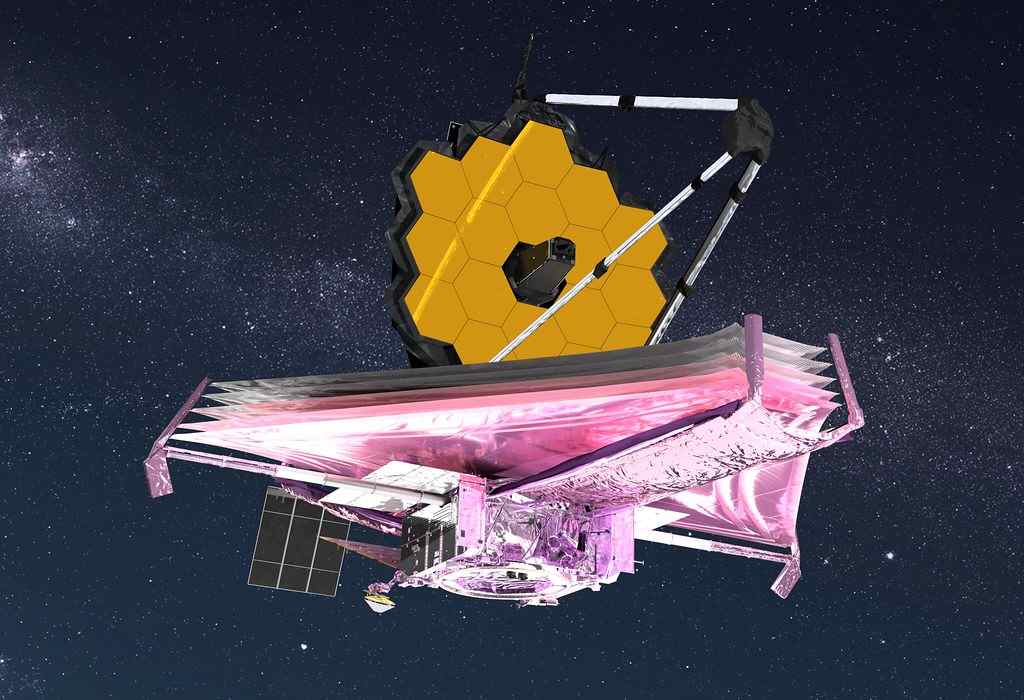
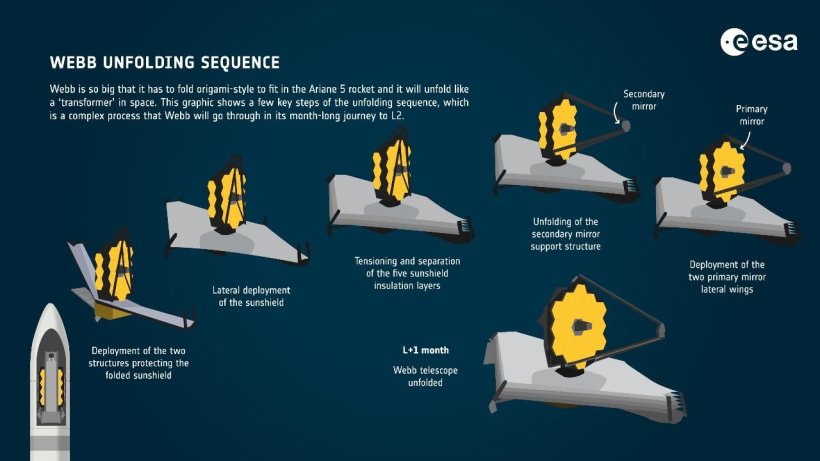
Webb will take roughly a month to reach the L2 point in orbit after launch. It will gradually unfold its most prominent feature, a vert ramp sunshield, as it travels there, starting a few days after the event.
The sun shield is designed to reduce the sun’s heat by more than one million times to -364 degrees F. Webb’s mirror and equipment must be cool at all times. If they were heated by the sun, they would emit infrared radiation. The Webb is designed to detect weak infrared signals from the distant universe.
NASA’s James Webb Space Camera has been remeasured.
After a few delays, the space agency has confirmed that it is again prepared for its scheduled liftoff before 2021. NASA, or the National Aeronautics and Space Administration, has announced that its engineering teams have completed all necessary testing for the James Webb Space Telescope.
As a result, the US space agency said that the $10 billion telescopes have resumed all launch preparatory procedures ahead of its much-delayed liftoff next month, according to The Register.
NASA’s James Webb Space Microscope issue has been rectified.
It’s worth noting that NASA’s expensive for another observatory was meant to launch on December 18th. However, an incident involving the unintentional release of its clamp band delayed its liftoff date back significantly. The unexpected and unexpected removal of the clamp ring from the James Webb Telescope caused shocks throughout the $10 billion telescopes.
As a result, NASA said that it will require several days to test the telescope for any potential damage caused by the sudden removal of the clamp band. Having said that, the US Space Agency went on to say that it has formed an anomaly review board to investigate the recent occurrence, which caused most of the observatories to vibrate.
In addition, NASA announced that the James Webb Orbit Telescope would undergo a series of tests to confirm that it is ready to go into space. It should be noted that the examination especially examines any harm produced by the most recent incident.
Also read: What is the life expectancy of the Hubble telescope?
The Webb Telescope has had a lengthy journey
The development of the Webb began in 1996, with a $500 million budget. The launch was originally scheduled for 2007, according to space scientists and engineers.
However, the project has been plagued by significant delays and cost overruns, and it underwent a substantial redesign in 2005. Following that, they expected to launch in March 2020, but the coronavirus pandemic occurred, causing substantial difficulties.
However, the team has recently made tremendous progress. According to NASA, existing program funding will allow the Webb to be completed within its current $8.8 billion cost constraint. The sunshield of a fully built James Webb Orbit Telescope successfully passed its own final testing, including a full unfolding, precisely as the telescope would need to perform once in space, in December 2020.
What is the duration of the Webb mission?
Webb is intended to have a mission lifespan of at least 5-1/2 years following launch, with the objective of having a lifetime of more than ten years. The amount of fuel consumed to sustain orbit and the correct operation of the spacecraft and equipment in orbit eventually restrict the lifespan.
Webb will carry enough fuel for a 10-year lifespan (plus margin); the project will complete mission security testing of the flight system that ensures 5 years of scientific activities commencing in 2015. 6 months after launch at the end of the commissioning period.
Conclusion
The James Webb Space Telescope, often known as Webb or JWST, is a massive space-based observatory tuned for infrared wavelengths that will complement and expand Webb Space Telescope findings. It will have a wider wavelength coverage and much higher sensitivity. Webb can scan further back in time to identify the earliest galaxies that formed in the early Universe, as well as gaze within dust clouds where stars and planetary systems are developing today, thanks to the longer wavelengths.
Resent posts: