The size of the universe has always presented a significant obstacle to human exploration and finding. Despite our natural curiosity and technological advancements, it would take us many years, if not centuries, to journey to the nearest star to our solar system.
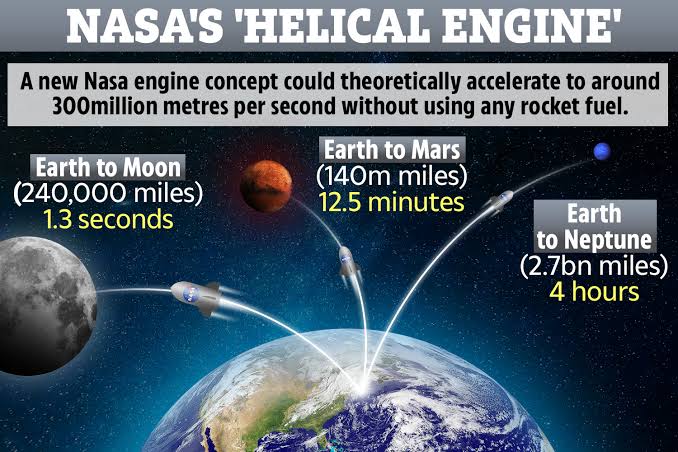
With his revolutionary engine idea, NASA engineer David Burns may have finally discovered the secret to accelerating spacecraft to an amazing 99% of the speed of light without the use of conventional propellants. The ultimate frontier might just become a little bit closer for us thanks to Burns’ creative solution.
NASA Engineer David Burns’ “Helical Engine”
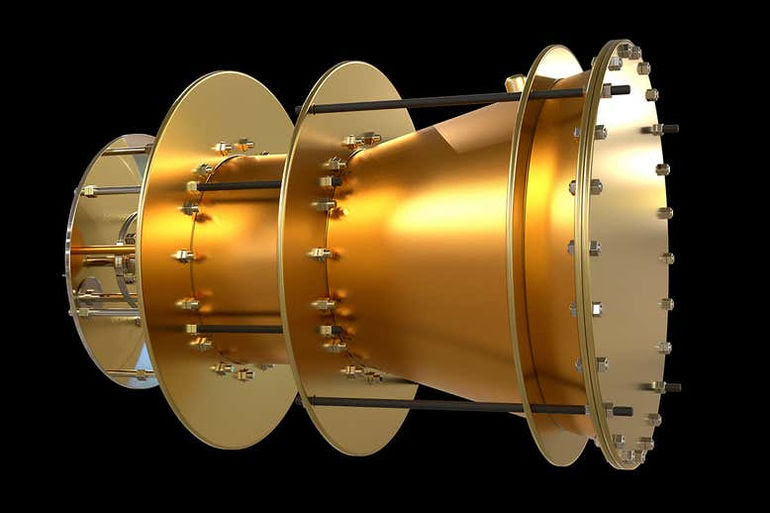
Since NASA engineer David Burns released his paper on the “Helical Engine” in the NASA Technical Reports Server, the scientific community has been on a high. The distinctive way mass can change at relativistic speeds—those that are close to the speed of light in a vacuum—is exploited by the engine.
It is crucial to remember that the paper has not yet been subjected to expert evaluation. It’s extremely unlikely that this idea will overturn the laws of physics anytime soon, despite the buzz and headlines saying the engine could “violate the laws of physics.”
Related: How Does the Helical Engine Work?
The concept of the Helical Engine
David Burns’ Helical Engine not only presents an interesting theoretical concept, but also comes with a fascinating visual demonstration. Imagine a box with a weight inside, suspended from a line and attached to springs at either end.
In a vacuum, the weight would remain stationary while the box wobbles around it – like a captivating gif that’s been stabilised around the weight. This concept has sparked the imagination of many science enthusiasts, as it illustrates the potential workings of the engine.
However, while the idea of the Helical Engine is exciting, it also challenges the laws of physics as we understand them. By increasing the mass of the weight in one direction, a greater push is generated, resulting in thrust. Yet, the conservation of momentum principle dictates that the momentum of a system remains constant in the absence of external forces, meaning that this concept may not be entirely feasible.
Exploiting a Special Relativity Loophole and the Engine’s Ineffciency:
Using a special relativity flaw, David Burns’ Helical Engine exploits the ability of objects to accumulate mass as they near the speed of light. The engine can alter the ions’ velocity to change their mass and produce propulsion by using ions in place of a weight and a loop in place of a box.
It’s an intriguing idea, but the engine would need a huge helical cylinder with dimensions of 200 metres long and 12 metres wide. Furthermore, to generate just 1 newton of thrust, 165 megawatts of electricity would be required. Therefore, despite the idea’s appeal, it is presently impractical because of its inefficiency.
Related: Elon Musk & NASA’s New Light Speed Engine Defies Laws Of PHYSICS
The Long Road Ahead for the Helical Engine’s Development
The Helical Engine has a special chance to flourish in the vacuum of space. David Burns thinks the engine could achieve 99% the speed of light given enough time and force. It’s an alluring possibility for those who aspire to travel to other stars; however, it would be completely impossible to consider it without first considering the possibility.
The Helical Engine is obviously far from ideal. Burns quickly points out the inefficiencies and warns that his work has not yet been subjected to expert review. Although it’s a fascinating idea, much work needs to be done before it can become a reality.
Conclusion:
The idea of a light-speed engine for interstellar travel may sound like science fiction, but it has attracted the attention of both scientists and space enthusiasts. Despite the fact that the Helical Engine developed by David Burns remains largely theoretical and faces significant practical challenges, it represents a significant step towards creating advanced propulsion systems for space exploration.
Developing a light-speed engine could hold the key to uncovering the secrets of the universe and ushering in a new era of space exploration. While the road ahead may be uncertain, it is innovation and perseverance that will help us push the boundaries of space travel even further.
