When it comes to space, the field is multidimensional and much wider. So much experimentation and investigation have been done, however, we have not explored even 1%. The vastness of space could be well understood from this fact. Amidst this, we have an X-RAY IMAGING AND SPECTROSCOPY MISSION (XRISM) that also serves as one of the important missions to understand space physics.
This article will shed light on the important aspects of this mission and the components/devices used by the probe/spacecraft, as well as the prospects of the mission.
History of X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission
- Formerly known as X-Ray Astronomy Recovery Mission (XRASM)
- The collaborative mission of JAXA/NASA with ESA participation
- Rebuild of Hitomi spacecraft that was lost in 2016 due to some mishappening in it.
- Due to the Hitomi accident and to prevent a further mishap, International Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS) has decided that the project will have a separate Project Manager and Primary Investigator.
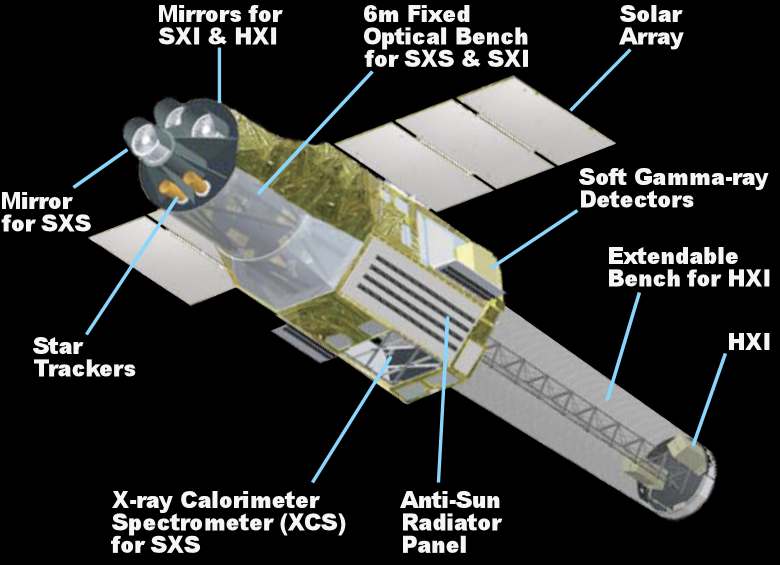
Instruments to be Used by Xrism Satellite
The XRISM will employ two instruments namely:
- RESOLVE: Basically, a combination of X-Ray Mirror Assembly (XMA) and X-RAY calorimeter spectrometer built to provide 5-7 eV of Energy resolution with a field view of about 3 arcmins in 0.3-12 keV bandpass.
- XTEND: A soft X-Ray imager having an array of four CCD detectors and can observe the space field up to 38 arcmins in 0.4-13 keV range.
Related: All you need to know Japan space agency’s mission to Mars’s moon
What are the Goals of Xrism?
- Scheduled to launch in 2023
- The mission will study various celestial X-Ray objects in space using High-resolution images and spectrography.
- XRISM will study all types of astrophysical objects that include interstellar space, neutron stars, various galaxies e.t.c.
- The mission also aims to answer various questions regarding the formation of space and dark matter.
- Similar to James Webb Space Telescope, and others of this period, XRISM will serve as the biggest achievement in the field of X-Ray astronomy
Conclusion
The accident with Hitomi (Astro-H) on June 14 2016 shocked the entire astronomical and space units on Earth. However, the manufacturing of XRISM satellite/spacecraft is serving as a solution to the loss of Hitomi (Astro-H).
XRISM is scheduled to launch into space in 202, and whether it will cover up the years lost due to the mishap of Hitomi (Astro-H) or not can only be answered after its successful entry into space.
FAQ related to (X-ray Imaging And Spectroscopy Mission)
Q- Why XRISM is being carried out?
Ans- The XRISM (X-RAY IMAGING AND SPECTROSCOPY MISSION) is a collaborative work of JAXA/NAXA, along with little participation of ESA (European Space Agency) to study space physics and unfold various mysteries of celestial bodies. It also aims to answer the queries related to the formation of space and dark matter.
Q- Why XRISM is being carried out?
Ans– The XRISM will fill the gap of loss that happened due to the mishap with the Hitomi (Astro-H) spacecraft in June 2016. Earlier, the project was known by the name X-Ray Astronomy Recovery Mission (XRASM).
Q- Which space organizations are working for XRISM?
Ans- “XRISM” is the collaborative work of JAXA/NASA along with little participation from ESA (European Space Agency).
Q- Which instruments will XRISM use to get accomplished successfully?
Ans- XRISM Observatory will have two instruments Resolve and Xtend to catch High-Resolution field view in space.