What is on the Earth? What structures are present on the Earth? What are the major domains of the Earth? We are going to cover these questions in this article.
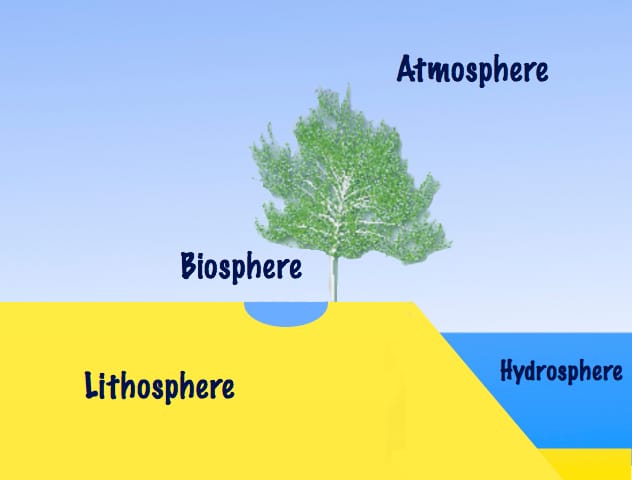
Imagine walking on a beach with water flowing to your feet and a cool breeze hitting your face. The water flowing is the Hydrosphere, the sand below your feet is the Lithosphere and the air striking your face is the Atmosphere. Thus, there are four major domains of Earth–
1. Lithosphere –
The solid portion on which we live is called the Lithosphere.
2. Hydrosphere –
The area covered by water is the Hydrosphere. It consists of seas, oceans, rivers, lakes, ponds and other water bodies.
3. Atmosphere –
The layer of gases surrounding the Earth is the Atmosphere. It consists of various gases such as oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, carbon dioxide and other gases.
4. Biosphere –
It is the zone that is made up of land, water and air together. Thus, Biosphere is the combination of the Lithosphere, Hydrosphere and Atmosphere.
Let us know about all these major domains of earth in detail!
More about Lithosphere
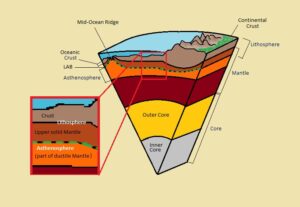
As you got to know, Lithosphere is the solid, uppermost portion of Earth or the land on which we live. The lithosphere consists of the upper layer of the mantle and the crust which are the outermost layers of the surface. The lithosphere is made up of rocks and thin layers of soil which contain the important nutrients for the growth of organisms.
The lithosphere is broken into tectonic plates. The movement of these tectonic plates leads to events like tsunamis or earthquakes. The level of seawater remains the same everywhere as the oceans are connected. The elevation of the land is measured from the sea level and the sea level is taken as zero.
The height of land is denoted by ASL (Above Sea level) or BSL (Below Sea Level). World’s highest mountain peak Mt. Everest is 8848.86 metres higher than the sea level whereas the deepest point of Mariana Trench is 11,022 metres deep in the Pacific Ocean.
The Earth has two types of lithospheres: oceans and continents. Continents are the large landmasses on Earth while the oceans are the large water bodies.
Continents
A continent is a large continuous landmass on Earth that may or may not be separated by water bodies. The Earth has seven continents. All the continents together make up one-third of the planet and the rest is covered by water.
Two-thirds of the continents are located in the Northern Hemisphere. The shape and borders of a continent are decided by the water bodies surrounding it. More water means less land.
The Seven continents of Earth in the order of their sizes are:
1. Asia
It is the largest continent and extends from the Mediterranean Sea to the west Pacific Ocean. Asia covers about one-third of the total land area of Earth and lies in the Eastern Hemisphere. There are more than 40 countries in Asia and consists of nearly 60% population of the world. The Ural Mountains separate the continent from Europe and the combined area of Asia and Europe is called Eurasia.
2. Africa
It is the second-largest continent and covers thrice the area as that of the United States. The Equator passes nearly through the middle of Africa. It is the only continent through which the Tropic of Cancer, the Equator, and the Tropic of Capricorn pass. Africa has the world’s largest hot desert, Sahara as well as the longest river, the Nile which is more than 6560 kilometres long. It is home to 56 countries but only 14% of the world’s population live in Africa.
3. North America
The third-largest planet, North America is linked to South America by a narrow land piece called the Isthmus of Panama. The continent lies completely in North West Hemisphere and includes the largest island of Greenland in the northeast.
4. South America
It is the next continent which lies in the Southern Hemisphere. It extends from the Caribbean Sea to the cold waters near Antarctic Circle. The longest mountain range, the Andes is situated in South America. It also consists of several volcanic areas and the largest river, Amazon.
5. Antarctica
Antarctica is a continent completely in the Southern Hemisphere. The South Pole is nearly at its centre. It is permanently covered with snow and ice as it is near the South Pole. It doesn’t have any permanent human settlements but many countries have research stations there. India’s research stations are named Maitri and Dakshin Gangotri.
6. Europe
It is the second smallest continent and contains just seven percent of the total land. But Europe’s population is more than twice of South America. It has more than 40 countries and many important cities. It is surrounded by the Arctic Ocean in the north, the Caspian Sea in the southeast, the Atlantic Ocean in the west and Black and Mediterranean Seas in the south.
7. Australia
It is the smallest, the flattest and the second driest continent, after Antarctica. It is surrounded by water bodies on all sides and is thus called an Island continent.
What is Hydrosphere?
Earth is popularly known as the ‘Blue Planet’ because of the blue colour of the water. Water on Earth covers more than 71% of the total land whereas the rest 29% is land. The hydrosphere is the domain of Earth which consists of all these water bodies.
All forms of water are included in the Hydrosphere. The liquid water is in oceans, lakes, seas, rivers, ponds, wells and groundwater. Vapours are in the form of clouds and fog. Ice is found in the form of glaciers and icebergs.
They all constitute the Hydrosphere. More than 97% of the available water is in oceans and is salty, thus unfit for use. A very small portion of water is available for humans for usage.
Oceans
The major portion of the Hydrosphere is made up of the Oceans. They are large water bodies that contain salty water. They are always moving in the form of tide, waves and ocean currents.
The Hydrosphere consists of five major oceans. They are:
1. Pacific Ocean
It is the largest ocean and covers about half of the total ocean land. It extends from the Arctic Circle in the north to the Antarctic Circle in south. It has nearly 25000 islands and the deepest point, Mariana Trench is also situated in the Pacific Ocean. It contains 50% of the total global ocean volume.
2. Atlantic Ocean
It is the second-largest ocean but still half as that of the Pacific Ocean. It is an ‘S’ shaped ocean and surrounded by North and South America to its west and Europe and Africa to the east. It is the ideal location for harbours and ports because of its indented and irregular coastline. It is also the busiest ocean.
3. Indian Ocean
The third-largest ocean, it is named after India. It covers up about 19.5% of the global ocean. It is a triangular-shaped ocean and is covered by Asia to the north, Australia in the east and Africa to the west.
4. Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean covers nearly 6% of the global ocean. The Pacific Ocean is nearly seven times larger than the Southern Ocean. It is named the Southern Ocean because of its position as it surrounds Antarctica.
5. Arctic Ocean
It is the smallest ocean and makes up only 4.3% of the total oceans. The Arctic Ocean is located in the Arctic Circle and surrounds the North Pole. It is bound by the northern boundaries of North America and Eurasia.
Atmosphere – The Domain of Air
The layer of gas which surrounds the Earth is called the Atmosphere. It is an important part of the planet as it provides us with the air we breathe and also protects us from the harmful UV rays of the Sun.
The atmosphere extends to a height of 1600 kilometres and is divided into 5 layers based on the temperatures, compositions and other properties. These layers are Troposphere, Stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere and exosphere.
- The atmosphere consists of 78% Nitrogen and 21% Oxygen which provides us with 99% of clean dry air.
- The remaining 1% is made up of other gases like carbon dioxide, argon and other gases.
- Oxygen, which makes up 21% of the atmosphere is the breath of life whereas nitrogen is useful in the growth of living organisms.
- Carbon dioxide is the other gas which is present in small amount but is essential for the growth of plants and absorbs the heat released by Earth.
Temperatures, pressure and density of the atmosphere change with height. The density is highest at sea level and decreases with height. This is the reason why climbers use oxygen cylinders to complete their needs for oxygen at greater heights.
The atmosphere also applies pressure which varies from place to place. Air moves from high pressure to low pressure and this moving air is called wind.
Biosphere: The Life Domain
The Biosphere is the domain where all three other domains – air, water and land meet. It is the zone of contact between them. Different species of organisms including humans are linked to each other and biosphere for their survival.
The biosphere is commonly divided into the plant kingdom and animal kingdom. The three domains interact with each other and affect everything on the earth.
- Cutting of forests for completion of our needs may lead to fast removal of soil from slopes.
- Natural calamities could change the earth surfaces to a large extent.
- A huge Tsunami could submerge islands completely.
- Waste disposal into rivers and oceans makes the water unfit for human consumption.
Global Warming

Carbon Dioxide is released from sources like industries, vehicles and power plants which pollute the air. Higher amounts of gas in the atmosphere leads to an increase in temperatures of the planet. This is termed as Global Warming. This makes the need to conserve the resources of the planet to maintain the balance between the various domains of Earth.
With the increase in global temperatures, the glaciers are melting at a faster rate and the sea levels are rising. The cloud forests are drying and wildlife is facing difficulty to keep alive. The levels of greenhouse gases, has been at the highest mark in the last 800,000 years.
The rise in greenhouse gases has led to faster climate changes than some species can adapt to. New changes have been difficult for survival for life. Earth’s ice cover in Greenland and Antarctica are melting too and it is predicted that by 2050, sea levels would rise by 1-2.3 feet all because of melting of glaciers
Since we have covered and learnt about all the major domains of Earth, we would like to test the knowledge you have gained so far. Below are some simple questions for you to test yourself.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. Which mountain range separates Asia and Europe?
1. The Andes
2. The Urals
3. The Himalayas
Answer – The Urals
Q2. What is the deepest point on the Earth?
Answer – Mariana Trench
Q3. Which is the third largest continent?
Answer – North America
Q4. Name the four major domains of the Earth.
Answer – Lithosphere, Hydrosphere, Atmosphere and Biosphere.
Q5. What is the position of the Indian Ocean based on the size?
Answer – Third
Let us know if you know their answers by writing them below in the comments section.