We always thought that space was a peaceful and quite place, where there’s nothing around. But what if I told you that space is not a calm and serene place, but is constantly experiencing storms of a different kind. Is it not fascinating? Rather than rain or snow, these storms involve powerful winds and magnetic waves that traverse through the vast expanse of space. This phenomenon is referred to as space weather.
Space Weather And The Sun:
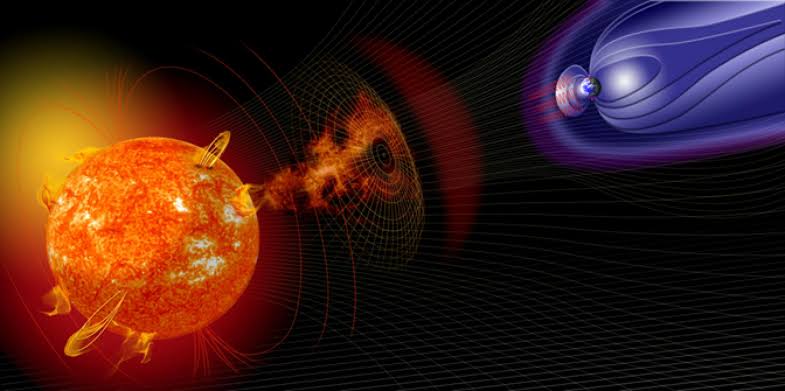
Space weather is a type of weather that originates from the activity on the Sun’s surface, which releases energy in the form of magnetic fields, particles, and electromagnetic radiation. Solar flares, Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs), and solar wind are some common space weather events. Despite the vast distance between the Sun and Earth, estimated to be around 93 million miles (150 million kilometers), space weather can still have a significant impact on Earth and the rest of the solar system.
Solar Wind And The Earth’s Environment:
The Sun continuously emits gas and particles into space, which collectively form the solar wind. This stream of particles originates from the outermost layer of the Sun’s atmosphere, called the corona, which is extremely hot. The particles in the solar wind are electrically charged due to their origin in the corona. They travel towards Earth at incredible speeds, reaching up to a million miles per hour. Thus, the solar wind is a constant feature of space weather that can affect Earth’s environment and technological systems.
Related: What are the 10 most abundant elements in the earth’s crust?
The Earth’s Protection:
Earth has an area of magnetic force activity which surrounds our planet and acts as a protective shield against the solar wind. Although some charged particles from the solar wind reach Earth’s magnetic field, the majority are deflected around it. However, the particles can cause compression and flattening of the side of the magnetic field facing the Sun, while the other side stretches into a long tail.
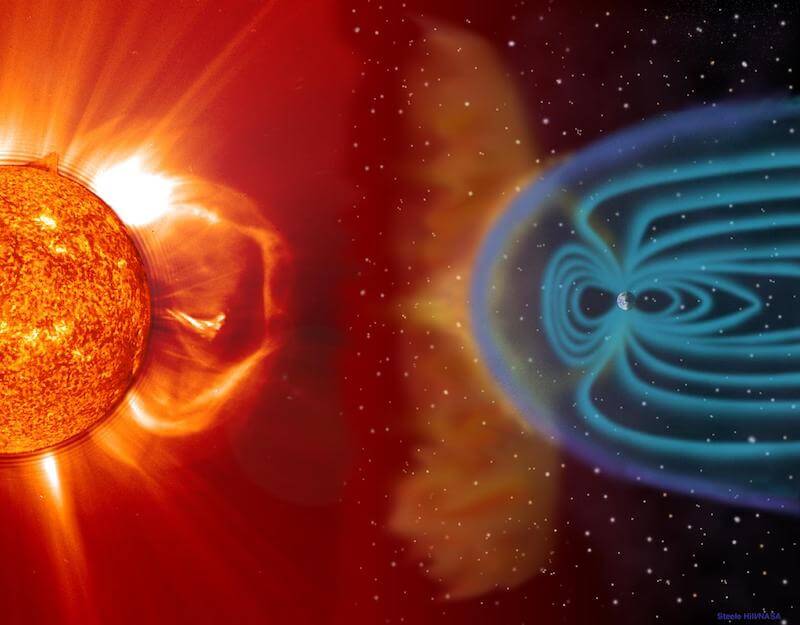
Related: What is Earth’s geological pulse?
The Effects Of Space Weather On Earth:
Despite Earth’s protective magnetic field and atmosphere, charged particles from the solar wind can occasionally penetrate and enter our atmosphere. When these particles collide with gases in the atmosphere, they create beautiful, luminous displays of light called auroras.
These natural phenomena, also known as the Northern and Southern Lights, can be seen in high-latitude regions such as the Arctic and Antarctic. Space weather has the potential to impact the Earth’s atmosphere and technological infrastructure. Space weather can also cause geomagnetic storms, radiation hazards, communication and navigation system disruptions, and power outages. In fact, in severe cases, space weather can cause damage to satellites and lead to electrical blackouts on Earth.
- Auroras
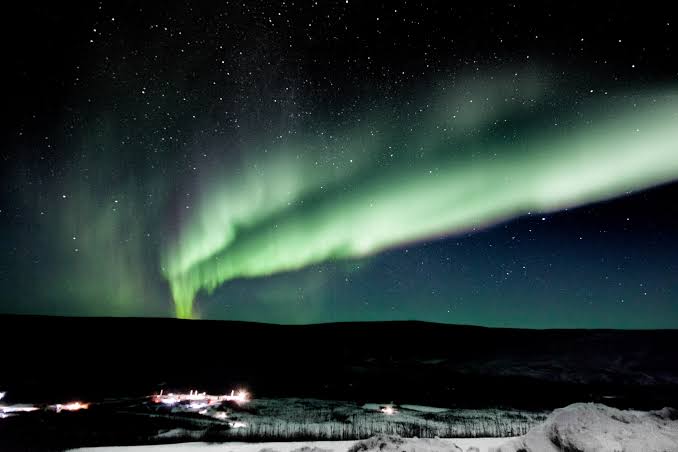

Auroras have a stunning and visible impact of space weather on Earth. They occur when charged particles from the solar wind interact with the Earth’s magnetic field and collide with gas molecules in the upper atmosphere, causing them to emit light.
- Geomagnetic storms:
Geomagnetic storms are a type of space weather phenomenon that occurs when the Earth’s magnetic field is disturbed by the influx of charged particles from the solar wind. These charged particles can interact with the Earth’s magnetic field, causing it to fluctuate and creating a geomagnetic storm.
Geomagnetic storms can cause a range of impacts on Earth, including disruptions to power grids, communication systems, and navigation systems.
- Radiation hazards
Radiation hazards are a potential impact of space weather, particularly from solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs). These events can release high-energy particles and radiation that can pose a risk to astronauts, satellites, and other space-based technology.
For astronauts, exposure to high levels of radiation from space weather can increase their risk of developing cancer and other health problems. In addition, space-based technology such as satellites can be damaged or destroyed by radiation, leading to disruptions in communication, navigation, and other critical systems.
- Communication and navigation systems can be disrupted by the ionosphere, a layer of charged particles in the Earth’s upper atmosphere that can absorb or scatter radio waves.
- Geomagnetic storms can induce electric currents in power grids, leading to transformer failures and blackouts.
Monitoring, Detection And Mitigation:
The effects of space weather on Earth can be disruptive and even dangerous. It is important to monitor and predict space weather to mitigate the potential impacts on human technology and infrastructure.
Space weather can be monitored using a variety of ground-based and space-based instruments that measure solar activity, the solar wind, and the Earth’s magnetic field. This data is used to develop space weather forecasts and alerts, which provide advance warning of potential space weather impacts.
Detection of space weather impact on technology can be achieved through monitoring of communication and navigation systems, power grids, and other critical infrastructure. By detecting anomalies and disruptions, operators can quickly respond and take mitigation measures to minimize the impact.
Mitigation strategies for space weather impacts can include a range of actions such as shielding sensitive equipment, adjusting spacecraft orbits, and developing new technologies that are more resilient to the effects of space weather. Additionally, response plans can be developed to minimize the impact on critical systems, such as power grids, and to ensure public safety during extreme space weather events
Conclusion:
Space weather is a natural phenomenon that can affect Earth in numerous ways, ranging from visually stunning auroras to potential power outages and damage to critical infrastructure. Therefore, ongoing monitoring, detection, and mitigation of space weather impacts are crucial for minimizing their consequences and safeguarding Earth’s technological systems and infrastructure. By staying informed and prepared, we can better manage the risks associated with space weather and ensure the safety and resilience of our society.