Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and one of our nearest celestial neighbors. However, it is not a particularly inviting area for Earthlings to visit.
If we assume that you’re an astronaut who has just landed on Mars, you should think about what are the most important things to live?
Here’s a brief list to get you started: Water, food, shelter, and oxygen are all necessities.
The air we breathe on Earth contains oxygen. It is provided to us by plants and some microorganisms.
However, oxygen isn’t the single gas in the atmosphere. It isn’t even the most plentiful. In fact, oxygen makes up only 21% of our atmosphere. The remaining 78 percent is almost entirely nitrogen.
Why Do We Not Breathe Nitrogen?
Now you might be thinking. If there’s more nitrogen in the air, why do we breathe oxygen only?
The technical reason is when we take a breath in, we take in everything in the environment. However, our body only uses oxygen, and we exhale to get rid of the rest.
Related: Here’s What Elon Musk Said When Questioned About The Life on Mars?
The Martian Atmosphere
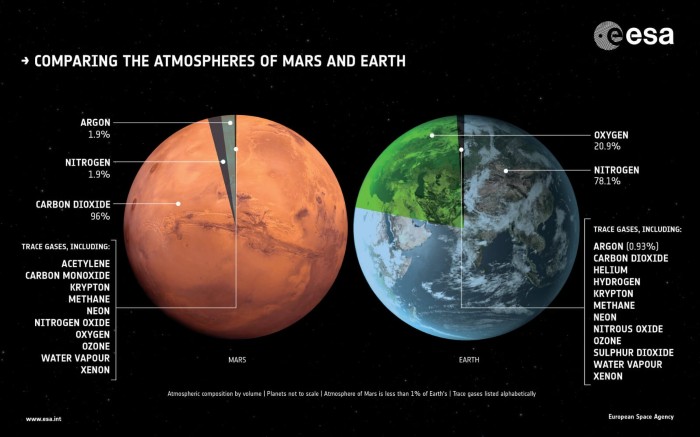
The Martian atmosphere is extremely thin, accounting for only 1% of the volume of Earth’s. In other words, Mars has 99 percent less air than Earth.
Part of this is due to the fact that Mars is roughly half the size of Earth. Its gravity is insufficient to prevent the escape of atmospheric gases into space.
What About Carbon Dioxide?
Carbon dioxide is the gas that is most plentiful in that thin air. This is a hazardous gas in high concentrations for people on Earth. It makes up less than 1% of our atmosphere, thankfully. Carbon dioxide, on the other hand, makes up 96% of the atmosphere of Mars.
What About Martian Oxygen?
There is essentially no oxygen on Mars; it makes up barely a tenth of one percent of the atmosphere, far too little for humans to exist.
You’d die in an instant if you tried to breathe on the surface of Mars without a spacesuit delivering your oxygen. You’d suffocate, and your blood would boil due to the low atmospheric pressure, all at the same time.
Related: Is There Any Evidence of Life on Mars? Let’s Explore
Can Any Organism Live On Mars?
So far, no evidence of life on Mars has been discovered. However, our robotic probes have only scraped the surface of the quest.
Mars has a harsh environment. It’s not just the air, either. The Martian surface has very little liquid water. The weather is bitterly cold, with temperatures dropping below -100 degrees Fahrenheit at night (-73 degrees Celsius).
However, many creatures on Earth are able to thrive in harsh settings. Life has been discovered in Antarctic ice, at the ocean’s bottom, and kilometres beneath the Earth’s surface. Many of those locations are extremely hot or cold, have little to no water, and have little to no oxygen.
It’s plausible that life existed billions of years ago on Mars, when the planet had a thicker atmosphere, more oxygen, warmer temperatures, and large volumes of liquid water on the surface.
Related: Mysterious Discovery On Mars Looks Just Like An Alien Doorway
Was There Any Alien Life on Mars?
One of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover mission’s goals is to search for signs of ancient Martian life. Perseverance is searching the Martian rocks for fossils of extinct species, most likely rudimentary life such as Martian microbes.
However, many creatures on Earth are able to thrive in harsh settings. Life has been discovered in Antarctic ice, at the ocean’s bottom, and kilometres beneath the Earth’s surface. Many of those locations are extremely hot or cold, have little to no water, and have little to no oxygen.
Even if life did exist on Mars billions of years ago, when it had a thicker atmosphere, more oxygen, warmer temperatures, and considerable volumes of liquid water on the surface, it is possible that it did.
One of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover mission’s objectives is to hunt for clues of ancient Martian life. Perseverance is looking for fossils of species that formerly lived on Mars, most likely primitive life such as Martian microorganisms, in the Martian rocks.
Read: Curiosity Vs Necessity: How can NASA produce Oxygen on Mars?
How Would We Breathe On Mars?
MOXIE, an extraordinary mechanism that absorbs carbon dioxide from the Martian atmosphere and converts it to oxygen, is one of the seven instruments on board the Perseverance rover.
If MOXIE works as expected, future astronauts will be able to produce their own oxygen as well as use it as a component of the rocket fuel they’ll need to return to Earth. The more oxygen people can produce on Mars, the less oxygen they’ll need to import from Earth, making it easier for tourists to arrive. Even if “homegrown” oxygen is available, astronauts will still require a spacesuit.
Conclusion
NASA is currently developing the new technologies required to transport humans to Mars. This could happen in the coming decade, possibly in the late 2030s. You’ll be an adult by then, and perhaps one of the first to set foot on Mars.
