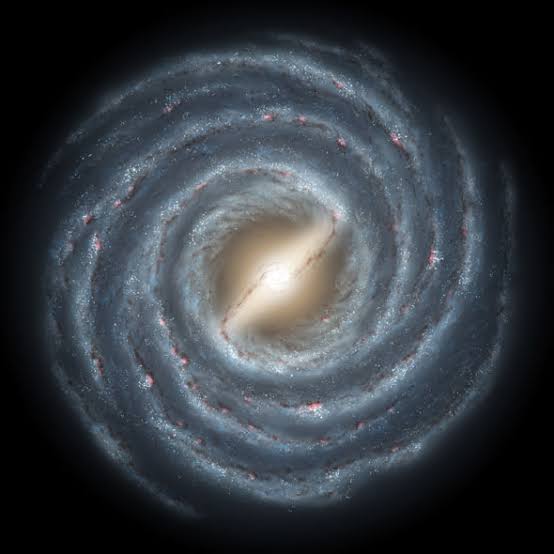
With lengthy rotating arms extending over the sky, the Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy that is around 13.6 billion years old. According to Las Cumbres Observatory, its disc is only 1000 light-years thick and roughly 100,000 light-years across.
Sagittarius A*, a supermassive black hole, is located at the centre of the Milky Way. Its mass is roughly 4 million times that of the sun, and it devours anything that gets too close.
By gorging on a plentiful supply of stellar material, it can grow enormously large. Though we cannot see this glutton in the centre of our galaxy firsthand, researchers can infer its existence by observing its impact on nearby matter.
How Old Is The Milky Way Galaxy?
Most galaxies have been in existence for between 10 billion and 13.6 billion years. Most galaxies formed when the universe was still very young; our universe is 13.8 billion years old.
Our own Milky Way galaxy is thought to be 13.6 billion years old, according to astronomers. Only 500 million years ago, the newest galaxy that we are aware of was formed.
The Most Distant Galaxy We Know
A galaxy dubbed GN-z11, which is 13.4 billion light-years away, was measured in 2016 by researchers using NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. This is because it is so far away, Hubble observes the light from the young galaxy as it was 400 million years ago, when the universe was just beginning.
How Big Is The Milky Way

To begin with, the Milky Way is enormous! Not only does it have a diameter of 100,000–120,000 light-years and a thickness of 1,000 light-years, but it also contains up to 400 billion stars (though some estimates think there are even more).
Related: How do we see light-years away?
Size Of Milky Way Galaxy In Kilometers
The diameter of the Milky Way galaxy is roughly 9.5 to 11.4 x 1017 km, or 9,500 to 11,400 quadrillion km, given that one light year is approximately 9.5 x 1012 km (9.5 trillion km) long.
It continued to consume other galaxies when it expanded to its present size and shape. Since the Milky Way’s disc is currently expanding, the Canis Major Dwarf Galaxy is actually the galaxy that is closest to it. And throughout its lengthy existence, our galaxy has eaten other objects, including the Sagittarius Dwarf Galaxy.
And yet, as compared to other galaxies in the immediate Universe, our galaxy is only a middleweight. The nearest massive galaxy to our own, Andromeda, is roughly twice as big as our own. It has a diameter of 220,000 light years and is thought to contain 400–800 billion stars.
Structure of the Milky Way
The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy, as may be seen if you were to leave the galaxy and gaze down on it from above. Long believed to have four spiral arms, the Milky Way now only appears to contain two, known as Scutum-Centaurus and Carina-Sagittarius, according to more recent surveys.
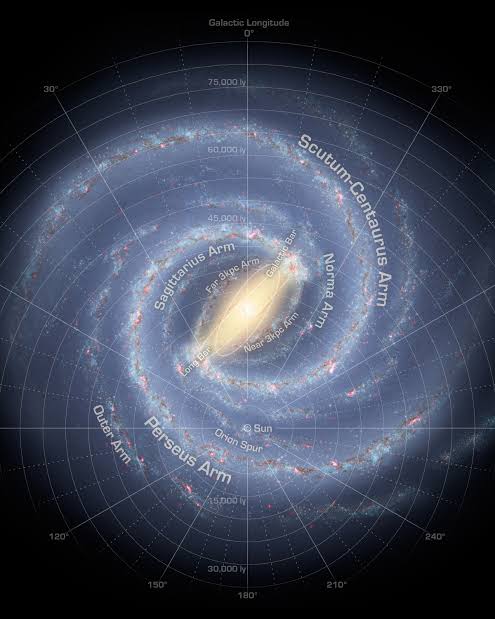
The Spiral Arms Of The Milky Way Galaxy.
The spiral arms are made up of grouped stars and gas clouds called density waves, which orbit the Milky Way. A period of active star formation occurs in the area as a result of the compression of gas and dust caused by these density waves as they pass through it.
However, by viewing portions of the Milky Way and other galaxies in our universe, scientists have been able to confirm the presence of these arms.
In actuality, none of the images that portray our galaxy were taken from a direct observation of the entire object; instead, they are either artistic renderings or images of other spiral galaxies. This is because we are inside the Milky Way.
It has been incredibly challenging for scientists to determine what it actually looks like. They have only been able to get a clear picture of what the Milky Way looks like from the outside after decades of observation, reconstruction, and comparison to other galaxies.
Related: What will happen when the Milky Way and Andromeda galaxy collide?
How Many Stars Are There In The Milky Way Galaxy?
Astronomers now calculate that there are between 100 and 400 billion stars in the Milky Way based on continual scans of the night sky with ground-based observatories and more recent space telescope missions.
There are likely hundreds of billions of planets in the Milky Way, billions of which are thought to be the size and mass of the Earth. They also believe that every star has at least one planet, implying that there are hundreds of billions of planets in the Milky Way.
As previously mentioned, dust and gas make up the majority of the Milky Way’s arms. The rest of the “luminous stuff” (i.e., that which is visible) in our galaxy is made up of stars; however, this matter only accounts for a stunning 10% to 15% of it. Only 6,000 light years of the visible spectrum can be seen inside the disc of our galaxy, which is about 100,000 light years across.
The hazy ring of the Milky Way can still be seen in the night sky when there is little to no light pollution. In addition, astronomers have been able to observe more of the Universe thanks to infrared astronomy and observations made of it in other, non-visible wavelengths.
Like all galaxies, the Milky Way is encircled by a large halo of dark matter, which makes up around 90% of its mass. Although the exact nature of dark matter is unknown, general behaviors and observations of the speed at which the galaxy rotates have been used to estimate its mass. More crucially, it’s thought that this mass prevents the galaxy’s rotation from splitting it apart.
The Solar System In Our Milky Way
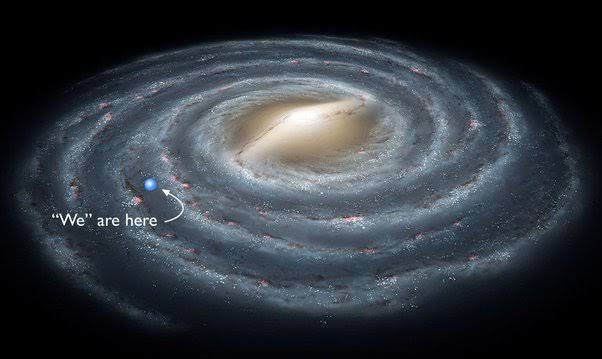
About 25,000 light-years separate the Solar System (including Earth) from the galactic fringe and from its center. Consequently, we would be located around midway between the center and the outside of the Milky Way, if you were to imagine it as a large record.
Where Is Our Solar System In The Milky Way Galaxy?
The Perseus arm and the Scutum-Centaurus arm are likely the Milky Way’s two largest spiral arms, together with a number of lesser arms and spurs, according to astronomers. The Orion-Cygnus arm is the area between the two arms where the Solar System is situated. This arm splits off from the Sagittarius Arm at a distance of 10,000 light-years and a width of 3,500 light-years.
The Solar System is believed to be close to the galactic plane because the Milky Way splits the night sky into two about equal halves. The gas and dust that populate the galactic disc give the Milky Way’s surface a comparatively modest brightness. We are unable to glimpse the brilliant galactic core or properly perceive what is on the opposite side of it as a result.
How Much Time Does the Sun Take To Complete One Rotation Around The Milky Way Galaxy?
You might be shocked to find that the Sun takes 250 million years to complete one rotation around the Milky Way; this is referred to as a “Galactic Year” or “Cosmic Year.” There were still dinosaurs on Earth the previous time the Solar System was in this location in the Milky Way.
How Far Is Earth From The Milky Way?
Astronomers and astrologers held the notion that the Earth was at the center of the universe for thousands of years. The fact that the Earth is a component of the Solar System confounded observations made from Earth, which contributed to this illusion.
We only learned that the Earth (and all other entities in the Solar System) actually orbit the Sun after many millennia of continuous observation and computations.
The location of our Solar System within the Milky Way is essentially the same. Actually, we’ve only been aware of our place in a much broader disc of stars orbiting a common core for the past century or so.
As because we are a part of it, it has historically been challenging to pinpoint our specific location. But because of continued work, astronomers now understand where our Sun is located inside the galaxy.
Distance of Sun From The Center Of The Milky Way
Almost all galaxies, as we now know, have such supermassive black holes at their centers. However, the real monsters can be much more massive, reaching masses of up to ten billion solar masses in the centers of the most massive galaxies. They can become active galactic nuclei or quasars when these black holes gorge on gas and dust.
The Galaxy Zoo team has spent the last 8 years studying the relationship between galaxies and their black holes, and throughout that time we’ve learnt a lot. We’ve learned a lot about black holes from Hanny’s Voorwerp, and your classifications of so many SDSS galaxies have significantly improved our comprehension of this “co-evolution”!
In the case of the Milky Way, we can observe the echoes of recent feeding outbursts from our black hole, from light echoes crossing the molecular clouds in the center to the mysterious Fermi bubbles, which many astronomers believe are the result of a strong burst of accretion by our black hole.
How Many Planets Are There In The Milky Way Galaxy?
In comparison to their actual separations, the planets, their orbits, and their host stars are all greatly enlarged. Planets around stars are more common than not, according to a six-year investigation that surveyed millions of stars using the microlensing method.
There are typically more than one planet per star. As a result, there are probably at least 1,500 planets within 50 light-years of Earth.
The findings are based on data collected over a period of six years by the 1995-founded PLANET (Probing Lensing Anomalies NETwork) partnership. According to the analysis, there are many more planets the size of Earth than bloated Jupiter-sized planets.
The basis for this is the calibration of a planetary mass function, which demonstrates that the number of planets rises for worlds with smaller masses. This survey’s preliminary findings suggest that there are more than 10 billion terrestrial planets in our galaxy.
How Can Astronomers Observe Objects That Are So Far Away?
Astronomers utilize light to observe distant objects. In fact, light even enables humans to travel in time!
A speed of almost 186,000 miles (300,000 kilometers) per second is the constant velocity of light. Accordingly, light can cover over 6 trillion miles (10 trillion kilometers) in a single year on Earth. This distance is measured in light years.
This implies that the length of time it takes for light from an object to reach us increases with its distance.
What Will Be The Future Of Humanity?
Humanity may no longer exist or it may have transformed into something altogether else.
You can see that the Milky Way alone is a large region. And figuring out where we are in it hasn’t been easy. And as our understanding of the universe has grown, we’ve discovered two things. In addition to being bigger than we could have ever imagined, the universe is getting smaller and smaller around us. It appears that our Solar System is both immensely valuable and unimportant in the larger scheme of things.
One of the roughly one hundred billion stars in the Milky Way, our sun travels in relative tranquility on the periphery of our own galaxy. The Milky Way’s center is located around 8 kiloparsec (26 thousand light years) away from Earth in the constellation Sagittarius.
Due to the massive volumes of gas and dust in the way, it can be challenging to see all the way to the center, but scientists have succeeded in breaking through this barrier to investigate the Milky Way galaxy’s core.
How Would Infrared Help To Track The Movements Of Stars?
Using cutting-edge infrared cameras, two astronomy teams—one from the University of California, Los Angeles and the other from Germany’s Max Planck Institute for extraterrestrial Physics—tracked the movements of stars right in the center of the Milky Way and discovered something extraordinary. All of the stars in our galaxy’s center revolve around the same void.
The stars appeared to be revolving around some large mass in the center. This mysterious object’s mass was determined to be four *million* times that of the sun. A black hole is the only thing that is both so little and so vast. Think of the monster hiding there the next time you see Sagittarius in the night sky.
What can we learn by studying distant galaxies?
Numerous galaxies at various distances have been seen by astronomers. We can start to comprehend the birth, evolution, and demise of galaxies and their stars by comparing them.
