Time is a unit of measurement of the continuous, unceasing change in our surroundings, typically seen from one particular angle.
While the idea of time is intuitive and self-evident—the events that steadily pass before our eyes; the Moon’s orbit around our planet—describing time’s underlying essence is significantly more difficult.
Even physicists are unsure of the precise nature of time. Nevertheless, they do have a few theories.
How Does Time Work?
Time was once thought of as a constant, autonomous force, as if the universe’s development was controlled by a single clock, for centuries.
With the introduction of Einstein’s theory of special relativity in 1905, He altered how time can be seen.
Although the relationship between space and time had long been understood, this groundbreaking idea was the first to unite them into a single field with measurements that changes depending on the gravitational pull or relative speed of the things it contained. In essence, this indicates that time is relative.
Related: What would happen to gravity if time stopped?
Is Time Real?
If two people are going at the same speed, they will both agree that the distance and time measurements are accurate. However, if one person changes their speed, they will observe a change in the other person’s perception of time and distance while their own remains constant.
This indicates that time isn’t even a constant, universal unit, as there is no justification for favouring one view of time over another. It is a relative measurement that changes as an object moves more quickly or slowly or experiences different amounts of gravity.
Space and time are curved by gravity, and time slows down the more strongly gravity is present.
The illustration below demonstrates how Earth’s mass bends space-time as an illustration of this.
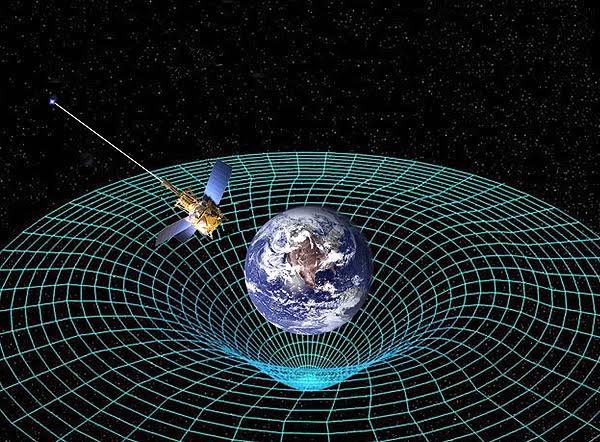
People on the International Space Station, which is farther from Earth’s gravity, age significantly more slowly as a result.
Related: How to create A Wormhole for Time Travel?
Is It Possible To Reverse Time?
Naturally, there must be a significant difference in speed or gravitational pull for us to truly observe these impacts on time. But when an observer moves closer to the speed of light, distinct measures of time become more obvious.
According to theory, we should observe a particle’s “clock” slowing down as it approaches the speed of light. Theoretically, after it approaches the speed of light, its clock would appear to be running backward from our perspective. Our clock would appear to go backward when viewed from the particle’s perspective.
Is Time Travel Possible?

Similar to how space is bent, time is also warped by the volume that extends beyond a black hole’s horizon.
We have complete freedom to roam around in our universe, but we are compelled to follow time’s arrow in a straight line.
According to calculations, switching such freedoms would occur if you crossed a black hole’s horizon. So while we wouldn’t have to adhere to time’s rigid arrow of direction, we would no longer have the ability to roam through space, which would prevent time travel.
While these hypotheses aid in our understanding of the nature of time, neither black hole nor light speed travel can be used to really turn back the hands of time due to certain limitations.
What Is This Space-Time?
Space-time models can explain how measurements of time and space change from one location to the next, but they don’t really explain why time clings so tenaciously to a series of events.
Our Universe is one space-time block according to these theories of time. The Big Bang might be thought of as a type of beginning before which it is impossible to apply the principles of physics. There is sort of a point at which change is no longer meaningfully assessed. However, no particular point in time physically stands out as “now.”
The distinction between the past, present, and future is merely a tenaciously persistent illusion, as those of us who believe in physics know, according to Einstein.
However, areas of physics other than cosmology may hold some secrets to the riddle of time. For instance, Austrian physicist Ludwig Boltzmann suggested a connection between time and an escalating degree of disorder in the universe back in the 1870s.
It suggested a potential explanation for why time travels only in one direction by connecting the thermodynamics’ concept of entropy to it: possibly our universe evolves from a low entropy, highly compact infant universe to a highly disordered, wide universe drifting into the future.
Conclusion
There is a way to slow down time, at least from your own perspective, that doesn’t involve travelling into space and escaping from Earth’s gravity well. This has nothing to do with the mechanics or nature of time itself, but rather with how each of us experiences the speed or slowness of life.
According to some researchers, being exposed to new situations or experiences can actually make time seem to move more slowly. The world seems to move more slowly when we’re young or learning something new, which may have something to do with the amount of information our brains have to take in and process. The days and years appear to fly by as we age and settle into routines.
The fact that time is a little more flexible than most of us believe it to be can serve as a reminder that we have the power to change how we perceive how quickly the days pass, even if only slightly.
